Integrationsregel
Schule
Grundformeln der Integration
Integral einer Summe
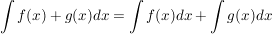
Integral mit konstantem Faktor
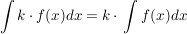
Integral der Potenzfunktion 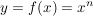
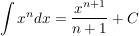 mit mit 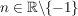
Integration durch Umkehrung der logarithmischen Differentiation
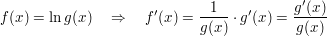
- Kehrt man die Differentiation um, so erhält man:
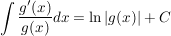
- Als Spezialfall für g(x)=x ergibt sich das Integral der Funktion
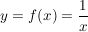 zu zu
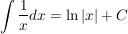
Integral einer Ableitungsfunktion
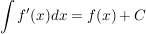
Integrale mit bekannten Funktionen
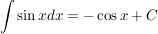
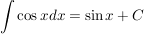
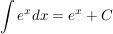
Definition partielle Integration
Die partielle Integration beruht auf der teilweisen Umkehrung der Produktregel der Differentiation. Deshalb wird die partielle Integration bevorzugt dort verwendet, wo Funktionen multiplikativ verknüpft sind.
Es gilt für f(x) = u(x) * v(x):
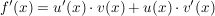
![$ \Rightarrow \int f'(x) dx = \int [ u(x) \cdot{} v(x) ]' dx = u(x) \cdot{} v(x) = \int u'(x) \cdot{} v(x) dx + \int u(x) \cdot{} v'(x) dx $ $ \Rightarrow \int f'(x) dx = \int [ u(x) \cdot{} v(x) ]' dx = u(x) \cdot{} v(x) = \int u'(x) \cdot{} v(x) dx + \int u(x) \cdot{} v'(x) dx $](/teximg/0/3/00387530.png)
ein wenig umsortiert ergibt sich:
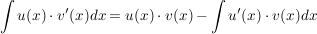
Beispiel
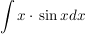
setze: 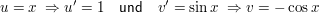
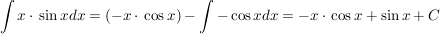
Integration durch Substitution
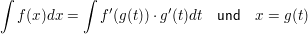
Beispiel
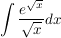
- Substitution:
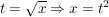 und dx = 2t dt und dx = 2t dt
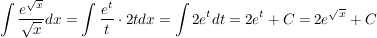
siehe auch Stammfunktion
Universität
|